Here's an example of adding an external A/D converter for
applications needing higher resolution and accuracy than the LabJack's 12-bit A/D inputs
provide.
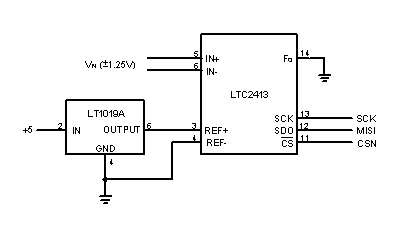
The circuit above uses a Linear
Technology LTC2413 24-bit A/D converter. The LT1019A is a 2.5 volt reference.
The LabJack SPI mode pin-out is shown in the following table.
| Signal |
LabJack Pin |
| MISI |
D14 |
| SCK |
D15 |
| CSN |
User selectable, D0-D7 |
The following sample code utilizes the LabJackWrapper class
to read the A/D.
LabJackWrapper labjack = new LabJackWrapper( -1 );
DecimalFormat fmt = new DecimalFormat( "#0.000000" );
int spiMode = 3;
int spiMsDelay = 0;
int spiHusDelay = 0;
int spiControlCS = 1; // >1 means we want LabJack to implement and control a chip select pin for us
int spiCsLine = 2; // '2' means use D2 as the chip select line
int spiCsState = 0; // specify active state (low) of chip select line, i.e. CSN
int spiConfigD = 1; // we want LabJack to configure I/O pins for us
labjack.configSPI( spiMode, spiMsDelay, spiHusDelay, spiControlCS, spiCsLine, spiCsState, spiConfigD );
LTC2413 adc = new LTC2413( 2.5f ); // using 2.5V reference
labjack.addSPI( adc );
while( true )
{
Thread.sleep( 100 ); // conversion time delay (plus LabJack SPI overhead)
labjack.updateSPI();
try
{
System.out.println( fmt.format( adc.getVoltage() ) );
}
catch( LTC2413Exception ex )
{
System.out.println( ex.getMessage() );
}
}
The LTC2413 class can be found here. |
